Comparing the Effectiveness of Mathematical Intelligence Enhancement Training and Storytelling-Based Problem-Solving Skills Training on Attention and Problem-Solving Skills in Children with Specific Learning Disabilities
Keywords:
Problem-Solving Skills, Storytelling, Mathematical Intelligence, Learning DisabilityAbstract
Purpose: This study aimed to compare the effectiveness of Mathematical Intelligence Enhancement Training and Storytelling-Based Problem-Solving Skills Training on improving attention and problem-solving skills in children with specific learning disabilities.
Methods and Materials: This quasi-experimental study employed a pre-test/post-test control group design. The statistical population included first-grade elementary school children with specific learning disabilities who were referred to a learning disability center in Khoy during the 2024–2025 academic year. A total of 45 students were selected through convenience sampling based on inclusion and exclusion criteria and randomly assigned to three groups: Mathematical Intelligence Enhancement Training (15 students), Storytelling-Based Problem-Solving Skills Training (15 students), and a control group (15 students). The interventions lasted for five weeks, with the math group receiving 15 sessions and the storytelling group receiving 10 sessions. Data were collected using the Conners' Continuous Performance Test to assess attention and the Problem-Solving Skills Scale to measure problem-solving skills. Data were analyzed using the Shapiro–Wilk test, one-way ANOVA, and Bonferroni post-hoc tests via SPSS-26 at a significance level of p < 0.05.
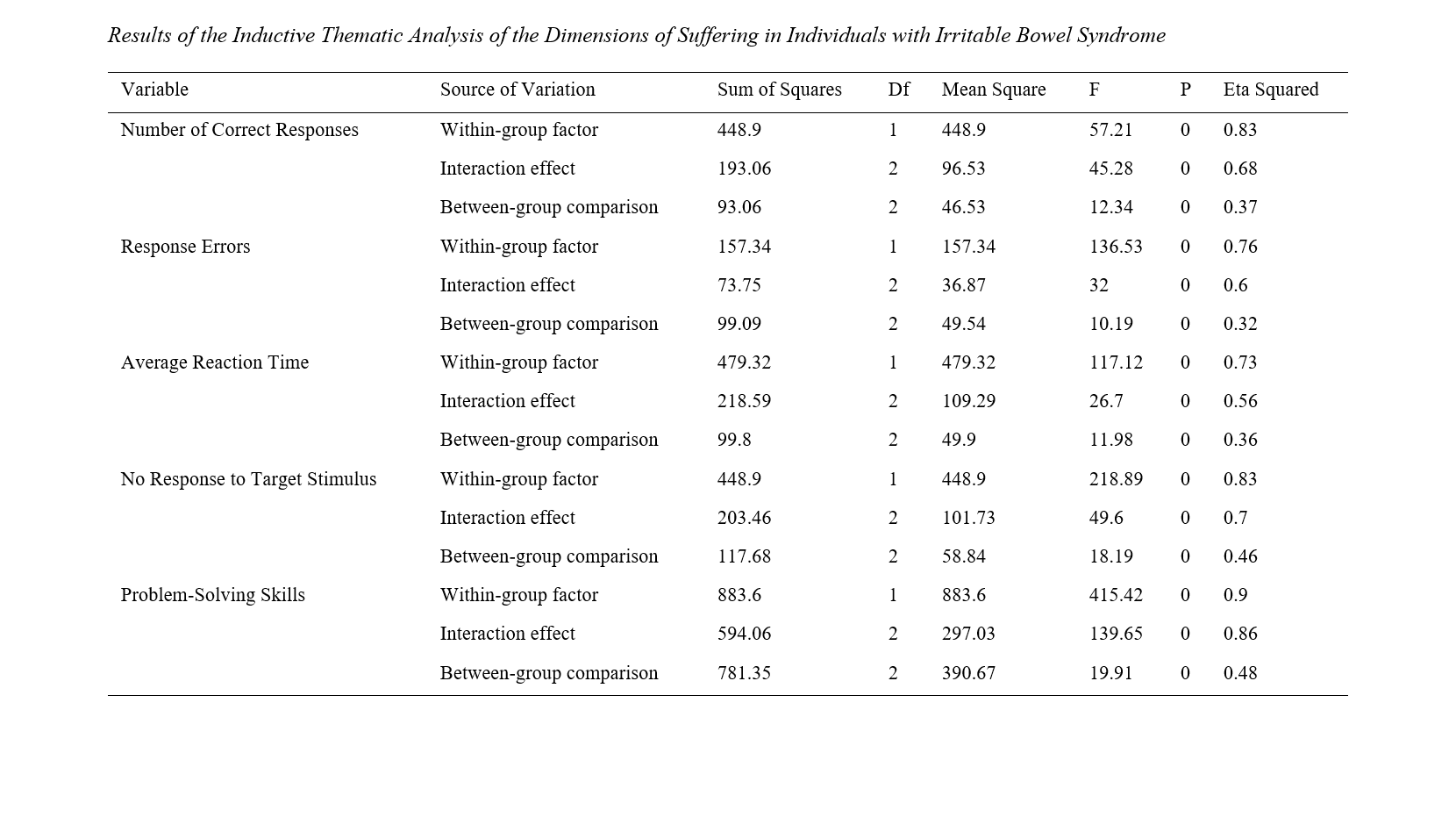
Findings: The results showed significant improvements in both attention and problem-solving skills in the two experimental groups compared to the control group (p < 0.001). Repeated measures ANOVA indicated significant intrapersonal, interactive, and interpersonal effects for all attention subscales and problem-solving scores. The storytelling-based group significantly outperformed the mathematical intelligence group in the number of correct responses, reduction of response errors, faster reaction times, fewer missed stimuli, and higher problem-solving scores (p < 0.05).
Conclusion: Both interventions were effective, but storytelling-based problem-solving training produced greater gains in attention and problem-solving skills, suggesting it as a superior instructional approach for children with specific learning disabilities.
Downloads
References
Altindağ Kumaş, Ö. (2024). The power of digital story in early mathematics education: Innovative approaches for children with intellectual disabilities. PLoS One, 19(4), e0302128. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0302128
Amin Abadi, Z., Hamid, A., & Soheila Ahmadi-Quchan, A. (2021). The effectiveness of a response-to-intervention-based educational program on the mathematical performance of third-grade elementary school students. Exceptional Children, 21(2), 117-128. https://joec.ir/browse.php?a_id=1356&sid=1&slc_lang=en
Arsalani, F., Sheikh, M., & HemaytTalab, R. (2019). Effectiveness of selected motor program on working memory, attention and motor skills of students with math learning disorders. The Scientific Journal of Rehabilitation Medicine, 8(3), 209-220. https://medrehab.sbmu.ac.ir/article_1100568.html
Bansal, G., & Singh, A. P. (2021). Computer-assisted cognitive re-training as an intervention for children with specific learning disability: A review. The International Journal of Indian Psychology, 9(4), 1038-1048. https://doi.org/10.31219/osf.io/wbt4f
Bartan, M. (2020). The Use of Storytelling Methods by Teachers and Their Effects on Children's Understanding and Attention Span. Southeast Asia Early Childhood, 9(1), 75-84. https://doi.org/10.37134/saecj.vol9.1.6.2020
Bayat, F., Rezaee, A. M., & Behnam, B. (2018). Comparison of the effectiveness of play therapy and storytelling on the improvement of Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder symptoms in students. Qom University of Medical Sciences Journal, 12(8), 59-68. https://doi.org/10.29252/qums.12.8.59
Bemana, S., Ghamarani, A., Naderi, F., Asgari, P., & Mehrabi, M. (2017). Compilation of Math Reinforcement Program Based on Response Pattern to Intervention (RTI) and it's Effectiveness on the Identification of Students with Special Math Disabilities. Empowering Exceptional Children, 8(3), 47-55. https://www.ceciranj.ir/article_64788.html
Bornstein, M. H., Hahn, C. S., & Wolke, D. (2013). Systems and cascades in cognitive development and academic achievement. Child development, 84(1), 154-162. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-8624.2012.01849.x
Bortolon, C., Lopes, B., Capdevielle, D., Macioce, V., & Raffard, S. (2019). The roles of cognitive avoidance, rumination and negative affect in the association between abusive supervision in the workplace and non-clinical paranoia in a sample of workers working in France. Psychiatry research, 271, 581-589. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psychres.2018.11.065
Chen, S. A., & Goodwill, A. M. (2022). Neuroplasticity and adult learning. Third international handbook of lifelong learning. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-67930-9_43-1
Ginting, D., Woods, R. M., Barella, Y., Limanta, L. S., Madkur, A., & How, H. E. (2024). The effects of digital storytelling on the retention and transferability of student knowledge. Sage Open, 14(3), 21582440241271267. https://doi.org/10.1177/21582440241271267
Irmayanti, M., Chou, L. F., & Anuar, N. N. (2025). Storytelling and math anxiety: a review of storytelling methods in mathematics learning in Asian countries. European Journal of Psychology of Education, 40(1), 24. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10212-024-00927-1
Jalilabkenar, S. S., Ashoori, M., & Movallali, G. (2012). Effectiveness of cognitive guidelines in improving mathematical problem-solving skills in female students with mental disability attending 3rd grade of middle school. Journal of Research in Rehabilitation Sciences, 8(3), 391-401. https://jrrs.mui.ac.ir/article_16554.html
Júnior, J. R. d. O., Limongi, R., Lim, W. M., Eastman, J. K., & Kumar, S. (2023). A story to sell: The influence of storytelling on consumers' purchasing behavior. Psychology & Marketing, 40(2), 239-261. https://doi.org/10.1002/mar.21758
Karami, A., Samie Zafarkandi, M., & Safarnavadeh, M. (2023). The educational model of the curriculum based on the storytelling method for students in the first year of elementary school. Qualitative Research in Curriculum, 4(13), 6-38. https://journals.atu.ac.ir/article_15470.html?lang=en
Kaveh, A., Hassan Zadeh, R., & Mirzaeian, B. (2021). The Effectiveness of Auditory Transformation Therapy with a Cognitive Information Processing Approach in the Treatment of Cognitive Dyslexia. Journal of Paramedical Sciences & Rehabilitation, 10(2), 58-71. https://jpsr.mums.ac.ir/article_18623.html?lang=en
Kenedi, A. K., Helsa, Y., Ariani, Y., Zainil, M., & Hendri, S. (2019). Mathematical connection of elementary school students to solve mathematical problems. Journal on Mathematics Education, 10(1), 69-80. https://doi.org/10.22342/jme.10.1.5416.69-80
Kolb, B., & Gibb, R. (2011). Brain plasticity and behaviour in the developing brain. Journal of the Canadian Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 20(4), 265. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3222570/
Mar, R. A., & Oatley, K. (2008). The function of fiction is the abstraction and simulation of social experience. Perspectives on Psychological Science, 3(3), 173-192. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-6924.2008.00073.x
Miller, S., & Pennycuff, L. (2008). The power of story: Using storytelling to improve literacy learning. Journal of Cross-Disciplinary Perspectives in Education, 1(1), 36-43. https://songsandtales.com/wp-content/uploads/The_power_of_story_using_storytelling_to.pdf
Mohagheghi, M., Pourmohamadreza-Tajrishi, M., Shahshahanipour, S., Movallali, G., & Vahedi, M. (2022). The effectiveness of assertiveness training on anxiety symptoms in school-age children with specific learning disorder. Archives of Rehabilitation, 22(4), 408-429. https://doi.org/10.32598/RJ.22.4.487.15
Mohammadlou, M., Sotoude Asl, N., Ghorbani, R., & Talepasand, S. (2024). The Effectiveness of Cognitive Rehabilitation on Improving Selective Attention, Cognitive Flexibility and Academic Progress of Students with Specific Learning Disorders. Journal of Applied Psychological Research, 15(1), 317-340. https://japr.ut.ac.ir/article_94180.html
Nasab, M. E., Faramarzi, S., & Sharifi, A. (2024). The Effectiveness of Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation along with Computerized Cognitive Training on the Executive Functions and Academic Performance among Students with Specific Learning Disorder comorbid with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder. https://asj.basu.ac.ir/article_5485_en.html
Şanal, S. Ö., & Elmali, F. (2024). Effectiveness of realistic math education on mathematical problem-solving skills of students with learning disability. European Journal of Special Needs Education, 39(1), 109-126. https://doi.org/10.1080/08856257.2023.2191110
Shahmohamadi, M., Entesarfooni, G., Hejazi, M., & Asadzadeh, H. (2019). The impact of cognitive rehabilitation training program on non-verbal intelligence, attention and concentration, and academic performance of students with dyscalculia. Quarterly Journal of Child Mental Health, 6(2), 93-106. https://doi.org/10.29252/jcmh.6.2.9
Treffinger, D. J., Isaksen, S. G., & Stead-Dorval, K. B. (2023). Creative problem solving: An introduction. Routledge. https://doi.org/10.4324/9781003419327-1
Vallefuoco, E., Bravaccio, C., Gison, G., Pecchia, L., & Pepino, A. (2022). Personalized training via serious game to improve daily living skills in pediatric patients with autism spectrum disorder. Ieee Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics, 26(7), 3312-3322. https://doi.org/10.1109/JBHI.2022.3155367
Wickens, C. (2021). Attention: Theory, principles, models and applications. International Journal of Human-Computer Interaction, 37(5), 403-417. https://doi.org/10.1080/10447318.2021.1874741
Wilterson, A. I., & Graziano, M. S. (2021). The attention schema theory in a neural network agent: Controlling visuospatial attention using a descriptive model of attention. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 118(33), e2102421118. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2102421118
Zilaey, S., Adibsereshki, N., & Pourmohamadreza-Tajrishi, M. (2017). Attention program and math performance of students with intellectual disability. Iranian Rehabilitation Journal, 15(4), 333-340. https://doi.org/10.29252/nrip.irj.15.4.333
Downloads
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Mahsa Asghari (Author); Ali Naghi Aghdasi (Corresponding author); Mahdi Aghapour, Alireza Aghdami Baher (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.

